Investing methods known as options strategies use option contracts to meet specific investment objectives. Options are financial derivatives that grant the holder the right—but not the obligation—to buy or sell an underlying asset at a defined price within a predetermined window of time.
Here are a few typical option trading strategies:
- Covered Call: With this technique, you sell a call option on an asset that you already hold the underlying. In addition to generating cash from the premium paid for selling the option, it offers some downside protection.
- Buy a put option: on an underlying asset as part of the protective put strategy to hedge against potential downside risk. It functions as an insurance policy, preventing losses in the event that the asset’s price drops.
- Long Call: By purchasing a call option, you have the right to purchase the underlying asset within a preset time frame at a set price (the strike price). When you believe the asset’s price will rise, you employ this tactic.
- Long Put: With this technique, you purchase a put option that grants you the right to sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price within a predetermined window of time. When you anticipate a decline in the asset’s price, you use it.
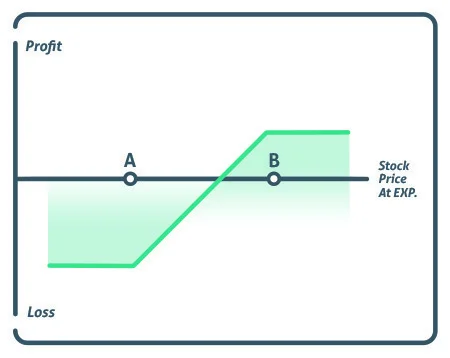
- Straddle: Buy both a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date when you straddle. When you expect considerable price volatility but are unsure about the direction of the price movement, you utilise this method.
- Strangle: A strangle is similar to a straddle in that it entails purchasing both calls and put options but with various strike prices. It is employed when substantial volatility is anticipated but with a preference for either an increase or decrease in the price of the underlying asset.
- The butterfly spread is a limited-risk, limited-reward trading technique that combines long and short call (or put) options at various strike prices. When you anticipate that the price of the underlying asset will stay within a certain range, you employ it.
There are many more sophisticated choice techniques available; these are but a few examples. Each strategy has a unique risk-reward profile and is suitable for various market circumstances. Before adopting any options strategy, it’s critical to have a clear understanding of the dangers involved with options trading and to take into account speaking with a financial advisor or other expert.
Why option trading strategies fail
It’s critical to comprehend the potential risks and difficulties involved with trading options because there are a variety of reasons why options strategies can fail. The following are some typical causes of option failures:
- Inaccurate Market Prediction: The success of option strategies frequently depends on the accuracy of the price forecast for the underlying asset. The technique could result in losses or have a limited possibility for profit if the market goes against expectations.
- Time decay: Options contracts have a deadline after which all of their value has been lost (time decay). Time decay, commonly referred to as theta decay, causes options to lose value over time. If the price of the underlying asset does not move in the predicted direction within the given time frame, the method may experience losses due to time decay.
- Inaccurate market forecasts: Options strategies frequently depend on forecasting the future course of underlying assets or the market as a whole. The technique might not succeed in producing the anticipated earnings if the projections prove to be inaccurate.
- Ineffective risk management: When trading options, effective risk management is essential. Strategies that improperly control risk can result in large losses. This includes failing to place proper stop-loss orders, failing to diversify the portfolio, or committing an excessive amount of capital to a single deal.
Conclusion
Option strategies can be useful instruments for risk management, revenue generation, and capturing market opportunities, to sum up. They do, however, come with their own dangers and cannot be guaranteed to be profitable in all market conditions.
Before employing any option strategy, it is essential to have a firm grasp of options, risk management theories, and market dynamics.
Since its efficiency varies on variables like market conditions, underlying assets, risk tolerance, and personal investing goals, there is no one-size-fits-all “most working” option strategy. Different approaches have different goals, and different investors may find them to be more or less suitable.
Other pages to consider reading
- “Option Volatility and Pricing: Advanced Trading Strategies and Techniques” by Sheldon Natenberg. Click here to find the version on Amazon.
- Options as a Strategic Investment” by Lawrence G. McMillan. Find it here
- Investopedia (www.investopedia.com)
- OptionsPlay (www.optionsplay.com)
#OptionsTrading #StockOptions #OptionStrategies #OptionsEducation #OptionsMarket #OptionsInvesting #OptionsTrader #OptionsIncom #VolatilityTrading #Derivatives