Introduction
Being ahead of the curve is essential for success in the quick-paced world of finance and investments. A trending market is a concept that can have a big impact on investment choices, resulting in significant gains or regrettable losses. In this thorough guide, we delve into the fundamentals of a trending market, including its traits, drivers, and potential-maximizing tactics. Join us as we investigate how to make profitable investments in a market environment that is trending.
Defining a Trending Market
A trending market, also known as a “bull market,” is a situation in which asset prices consistently increase over a protracted period of time. Positive market sentiment, economic expansion, and investor optimism are what are powering this upward momentum. Such markets provide the best conditions for investment growth because the prevailing trend tends to obscure momentary price declines.
Characteristics of a Trending Market
1. Positive Investor Sentiment
Investors display a high degree of confidence in the economy and the securities they own when the market is trending. This attitude is fueled by good news and earnings reports, which increases demand for assets and pushes prices higher.
2. Increased Trading Activity
A trending market experiences increased trading activity as buyers rush to take advantage of buying opportunities. The increase in trading activity strengthens the bullish trend and adds to the market’s overall liquidity.
3. Steady Economic Growth
Underlying a trending market is a robust economy that fosters favorable conditions for businesses to thrive. Low unemployment rates, increasing consumer spending, and stable GDP growth are indicative of a flourishing trending market.
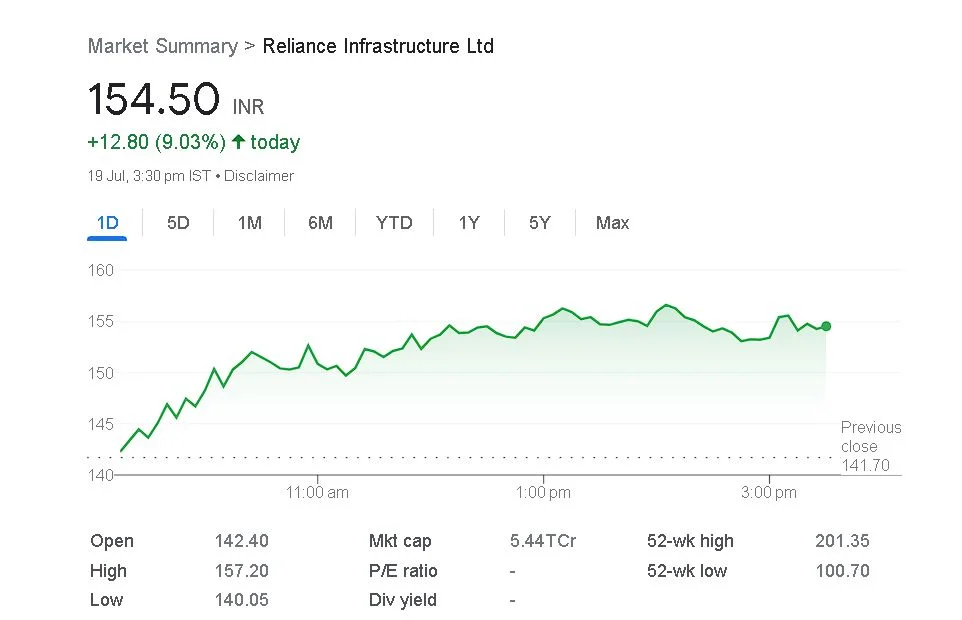
4. New Market Highs
The regular setting of new market highs is a key indicator of a trending market. As it continues to break records, this phenomenon shows how resilient the market is.
Factors Influencing a Trending Market
1. Economic Indicators
Economic indicators that influence a market’s trend include GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation. Investor excitement is frequently sparked by positive economic data, which supports the upward trend.
2. Monetary Policy
A market that is trending can be significantly impacted by the actions and monetary policies of central banks. Economic growth can be boosted by quantitative easing and lower interest rates, creating a positive environment for investors.
3. Corporate Earnings
Positive sentiment in a trending market is boosted by positive corporate earnings reports. Companies that consistently outperform analysts’ earnings forecasts draw more investors and drive the market higher.
Strategies for Capitalizing on a Trending Market
1. Diversification
Your investment portfolio’s diversification across different asset classes can help reduce risks during erratic market conditions. You can position yourself to profit from a trending market while limiting potential losses by diversifying your investments across stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
2. Trend Following
Using a trend-following strategy entails spotting and adhering to the current market trend. Moving averages and trendlines are two technical analysis tools that can help identify upward price movements and potential entry points.
3. Long-Term Investing
A trending market works well with a long-term investment strategy. You can ride the growth and compound your returns over time if you hold onto fundamentally sound investments for a long time.
Conclusion
Investors looking for significant returns have a wide range of opportunities in a trending market. A favorable environment for flourishing investments is fostered by increased trading activity, a rise in investor confidence, and steady economic growth. Investors can benefit from the upward momentum by making wise decisions by understanding the traits and forces influencing a trending market.
To successfully navigate the dynamic nature of financial markets, keep in mind that while a trending market can result in profitable outcomes, it is crucial to conduct careful research, diversify your investments, and follow a clearly defined strategy.
FOR MORE INFO CLICK THIS SITE:https://learningsharks.in/
FOLLOW OUR PAGE:https://www.instagram.com/learningsharks/?hl=en