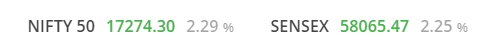25 Stock Market Terms That You Should Know
Firstly, Understanding the stock market can be seen as a challenging task. Some confusing terms and concepts will frustrate you, but being familiar with these terms will surely help you.
Secondly, These stock market terms will improve your stock market vocabulary and help you become a better and more successful investor.
So let us understand these 25 essential stock market terms that every investor should know:
Annual report
Importantly, Every corporation creates an annual report each year to impress its shareholders. A company’s annual report contains a wealth of information, from cash flow to managerial philosophy.
Many people read the annual report to assess the viability of the business and its financial standing.
Arbitrage
Undoubtedly, Arbitrage is the practice of buying something, such as foreign currency, from one location and selling it to another location where the foreign currency will fetch a greater price than the initial location.
For instance, if a stock is trading for $20 in one market and $21 in another, the trader must purchase shares at $20 in one market and sell them for $21 in the other market to profit from the price difference between the two markets.
Averaging down
Moreover, When an investment is averaged down, more stock is purchased when the price of a particular stock declines. The average price paid for your particular stock drops as a result.
This approach is employed by many investors who believe that the consensus of a particular company is incorrect and who anticipate that the stock price will increase as a result.
Bear Market
Indeed, It is a market where investors discuss how the stock market is currently behaving in a downward trend or when the values of several equities are falling at the same time.
Broker
A broker is a person that purchases and sells investments on your behalf and receives a commission or fee in return.
Dividend
A dividend is a term used to describe the quarterly or annual distribution of a specific amount of a company’s profit to its shareholders or stockholders. Furthermore, You won’t likely receive any dividends if you invest in penny stocks because not every company pays them.
Sensex
The Bombay Stock Exchange’s Sensex index is a number that represents all the relative share prices listed there.
Nifty
The principal and fundamentally based stock market index for the Indian equities market is the Nifty 50 Index, also known as the National Stock Exchange of India.
The Nifty 50 is one of two stock indices that are primarily used in the stock market, and it comprises 50 Indian corporate stocks in 12 distinct sectors.
Quote
The stock’s latest trading prices contain information that is given in a quote. Sometimes, the quote is delayed by 20 minutes unless you’re an actual stockbroker working in an existing trading platform.
Share Market
A share market is a marketplace where shares of a certain business can be bought and sold. A clear illustration of a share market is the stock market.
Bull Market
It is a market where investors discuss how the stock market is doing in an upward trend or when the values of several equities are rising at the same time.
Bid Price
A bid price is nothing but the amount that you desire to pay for a particular share.
Ask Price
The price at which you are looking to sell a share is known as the “ask price.”
Order
Order refers to the intention of buying and selling shares within a certain price range. For instance, you have placed an order with firm A to purchase 200 shares for a maximum price of Rs 50 each.
Trading Volume
Trading volume means the number of shares that are traded on a particular day.
Market Capitalization
It merely refers to a company’s valuation as determined by the stock market. That represents the total market value of all outstanding shares of a corporation.
Intra-Day Trading
Intraday trading means buying and selling your desired stocks on the same day so that before trading hours get over, all your trading positions will be closed within the same day.
Market Order
An order to purchase and sell shares at the current market price is known as a market order. In addition, Due to the continued volatility of the trading price in the market order, many investors choose not to follow this Order.
Day Trader
In spite of this, A day order is valid through the close of business. The Order will be canceled if it doesn’t fulfilled by the time the market closes.
Limit Order
Using a limit order, Still you can acquire shares at a lower price and sell them at a higher price. To trade shares, it is advisable to utilize a limit order.
Portfolio
The portfolio is a compilation of all the investments a shareholder has made Or starting with their initial share purchase.
Liquidity
Liquidity refers to how rapidly equities can be traded off. So, Shares that trade often and in big numbers are referred to as highly liquid.
IPO
Actually, By releasing its shares to the general public for the first time, a private firm becomes a public company and undergoes an IPO. The investor can purchase the shares directly from the company in the event of an IPO.
Secondary Sharing
Hence, It is yet another offering utilized to increase stock sales and public revenue.
Going Long
At Last, Betting on a stock’s price to rise, allowing you to acquire at a discount and sell at a premium.