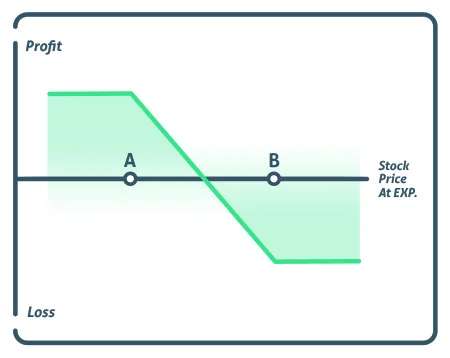
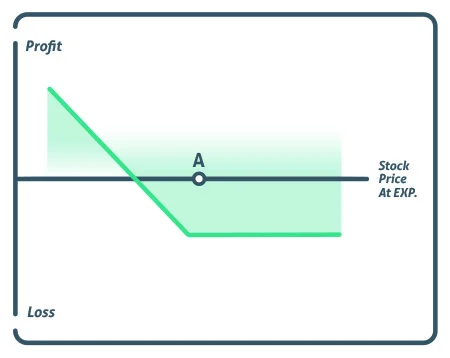
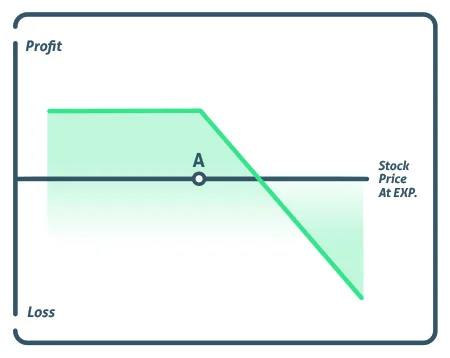
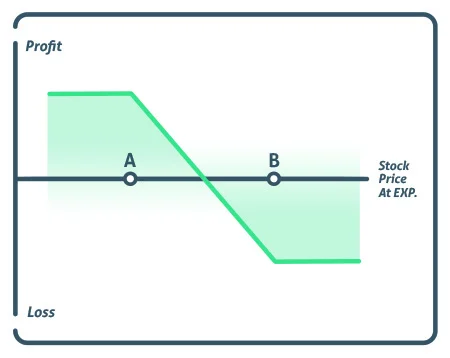
A bear put spread is a vertical spread in which you are long the higher strike price put and short the lower strike price put, both of which expire in the same month.
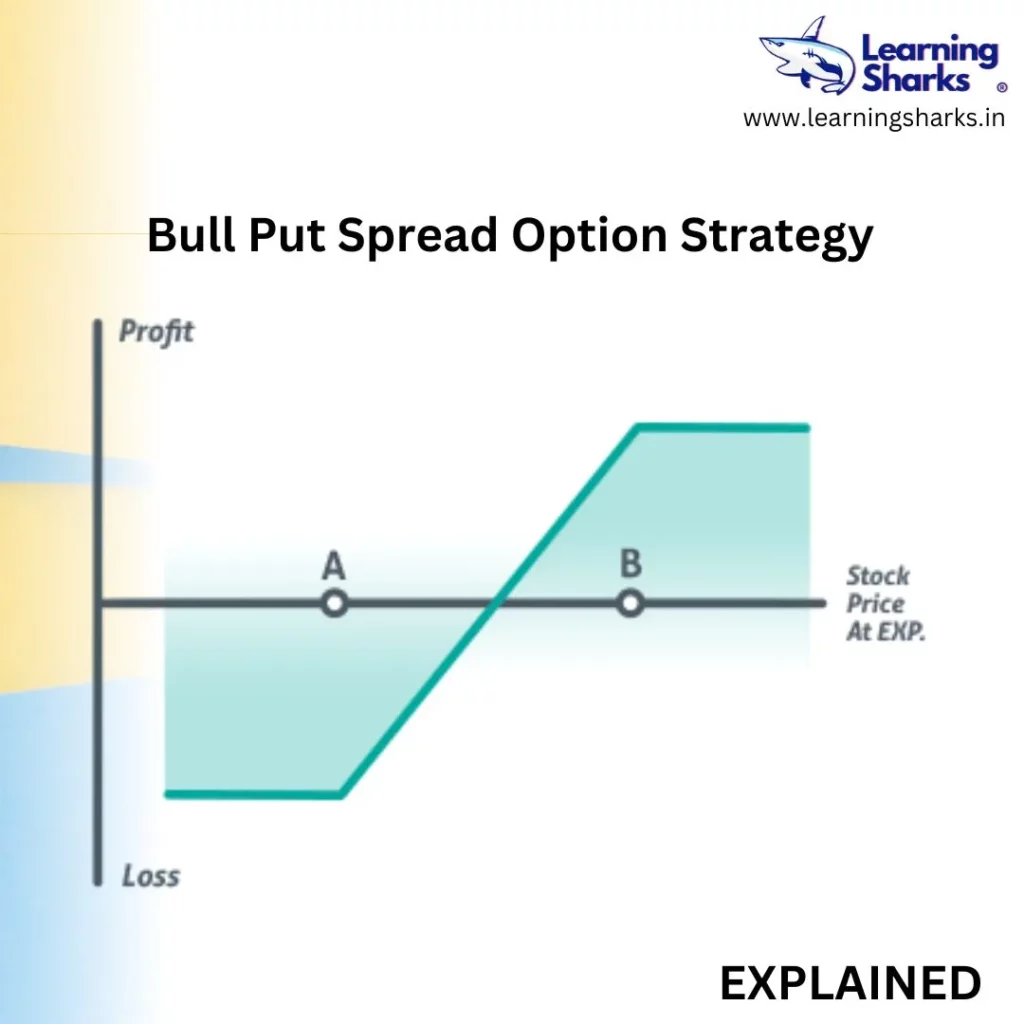
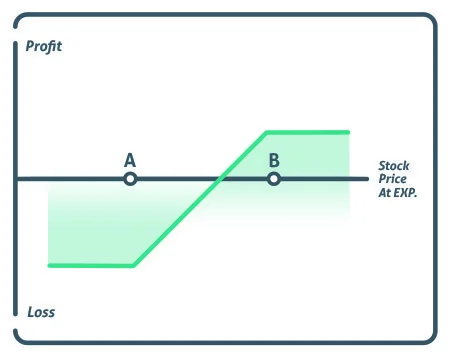
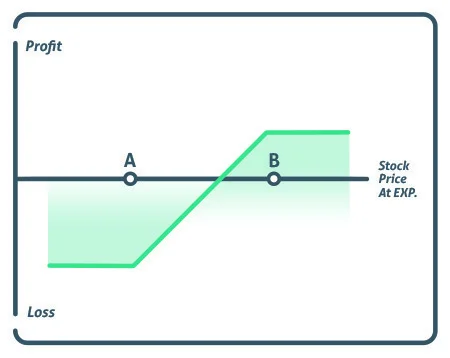
The strike price of the short strike, represented by point A, is lower than the strike price of the long put, represented by point B, implying that the investor will always have to pay for the deal. The fundamental goal of the short put is to help pay for the upfront cost of the long put.
Profit/Loss
A bear put spread’s maximum profit is derived by subtracting the difference between the two strike prices from the premium paid. At expiration, the strike price falls below the lower strike price.
The maximum loss is the trade’s cost. At expiration, the stock must trade over the upper strike price.
Breakeven
The breakeven point for a bear put spread is the higher strike price minus the trade cost.
Breakeven = long put strike – debit paid
Example
A Rs.2.50 bear put spread would consist of buying a 50-strike price put and selling a 40-strike price put, with a Rs.10 wide strike width (50-40), which is the maximum profit the investor could make on the trade, minus the premium paid to enter the trade, in our example Rs.2.50, leaving the investor with a maximum profit of Rs.7.50.
If this put spread is out of the money, time decay works against the investor because they need more time for this transaction to become lucrative. If the vertical has both strikes in the money, time would be on the investor’s side since they would want this transaction to end as soon as possible so that there is no more time for it to go against them.
Conclusion
This is not a method that should be used frequently until there is indication of an expected downward swing.
Without that, it’s a lower-probability strategy that relies on the stock falling in price before the expiration date. It needs less capital to engage than merely acquiring shares, implying lower risk, but it is still seen as a trade with a lower possibility of success.
FOLLOW OUR WEBSITE FOR CHART PATTERNS: https://learningsharks.in/chart-patterns/
Follow us on insta” http://learningsharks