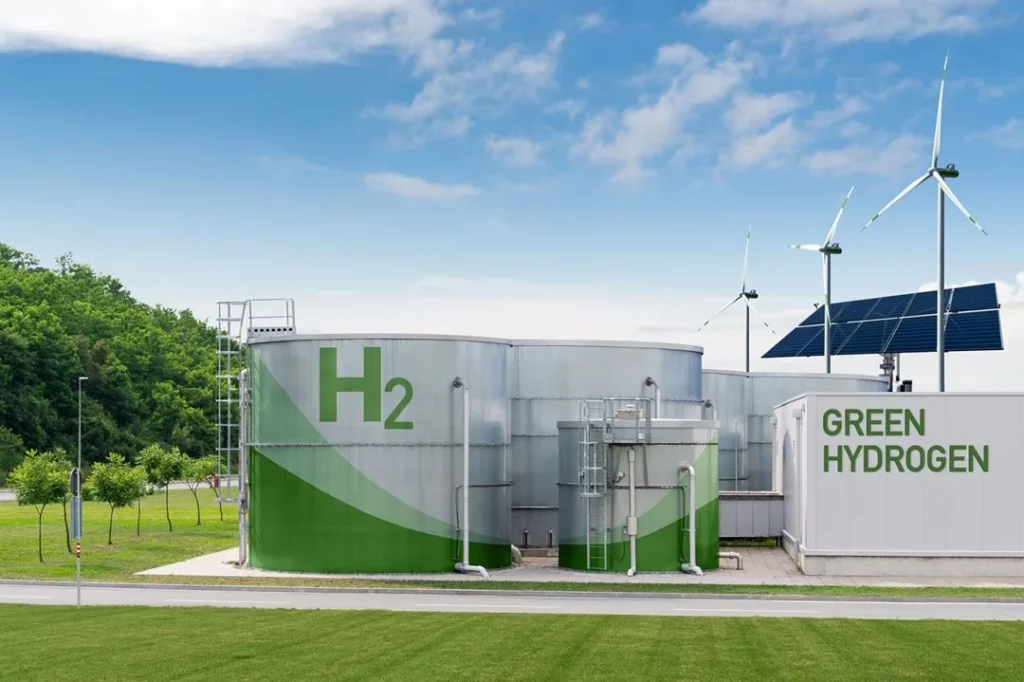
Green hydrogen was a budding industry in India as of my most recent knowledge update in September 2021, and things may have changed since then. It’s critical to undertake extensive research and take the most recent market trends and news into account when investing in stocks, especially in rising industries like green hydrogen. As of my most recent update, the following Indian businesses were active in the green hydrogen industry:
- Reliance Industries Limited (RIL): RIL has made plans to invest in the creation of eco-friendly hydrogen generation technologies. They have been concentrating on clean technologies and renewable energy.
- Adani Green Energy Limited: The Adani Group has been adding hydrogen project to its portfolio of renewable energy sources. One of the businesses in the group to keep an eye on is Adani Green Energy.
- Indian Oil Corporation (IOC):The largest oil and gas company in India, Indian Oil Corporation (IOC), has expressed interest in distributing and producing green hydrogen as part of its sustainability efforts.
- NTPC Limited: To supplement its current activities, NTPC, India’s largest power producing business, has been looking into green hydrogen projects.
- Tata Power Company Limited:Green hydrogen may present chances for Tata Power Company Limited, which has worked on a number of renewable energy initiatives.
- GAIL (India) Limited: GAIL is researching the viability of manufacturing green hydrogen and has expressed interest in the hydrogen industry.
- Larsen & Toubro (L&T): L&T is a significant engineering and construction firm in India that has worked on a variety of infrastructure projects, including ones involving hydrogen.
Please be aware that since my previous update, these companies’ plans and current state may have changed, and India’s green hydrogen industry may now be very different. Before making any investment decisions, it’s critical to review the most recent news, financial reports, and announcements from these companies. You should also think about speaking with a financial professional or conducting your own research. As the market evolves further, you might also wish to research recent competitors and startups in the green hydrogen space.
FOR MORE INFO CLICK THIS SITE:https://learningsharks.in/
FOLLOW OUR PAGE:https://www.instagram.com/learningsharks/?hl=en