The Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) oversees the Indian Energy market (IEX), an electronic power trading market established in India.
India’s leading energy market, Indian Energy Exchange, offers a national automated trading platform for the physical delivery of power, renewable energy, and certificates. In an effort to develop a fully integrated South Asian Power Market, IEX has more recently led the way in cross-border electricity exchange. Modern, user-friendly, and customer-focused technology powers IEX, enabling effective price discovery and enhancing the simplicity of power purchase.
With 7,300+ participants spread across 29 States and 5 Union Territories, including 1,800+ RE generators and obligated entities, 600+ conventional generators, and 55+ distribution utilities, IEX has a strong ecosystem. Additionally, it has a sizable network of 4600+ commercial and industrial clients, including those from the metal, food-processing, textile, cement, ceramic, chemical, automotive, information technology, institutional, residential, and commercial real estate sectors.
IEX has been in operation since June 27, 2008, and the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission has approved and regulated it. As of October 2017, IEX is a publicly traded corporation with the NSE and BSE.
Since August 2016, The Exchange has been accredited by ISO for quality management, information security management, and environmental management.
Who is the Director of IEX?
Rajeev Gupta holds a BTech from IIT BHU and an MBA from IIMA. He has 39 years of work experience, including 29 years in the financial services industry and 10 years in senior management positions in industrial firms.
With operations in M&A investment banking and private equity buyouts, Mr. Gupta formed Arpwood Financial Group in 2012. He formerly held positions as joint managing director of DSP Merrill Lynch (from 1995 to 2005), partner of the Carlyle Group, and head of India buyouts. Mr. Rajeev Gupta had held executive positions in industrial industries before joining DSP Merrill Lynch.
Mr. Gupta serves on the boards of United Spirits Ltd., EIH Ltd., T.V. Today Network Ltd., Vardhman Special Steels Ltd., Rane Holdings Ltd., TVS Capital Funds Ltd., and SBFC Ltd. as an independent non-executive member. He is a member of Bain & Co. India Ltd.’s advisory board.On April 27, 2022, he became a new Independent Director for our company.
How Does Trading Work On the IEX?
For instance, Bangalore is experiencing a power crisis, which would push up electricity prices and reduce the electricity board’s revenues. The electricity board will then use IEX to see whether there is a lower-priced electricity board, transmission firm, or renewable energy provider. After then, that segment will be put up for auction. Bangalore’s electrical board will be able to buy electricity more cheaply in this method. In addition, the organisation that sold the electricity will be able to turn a profit.
The IEX trades its products on a standard demand-supply basis. The IEX trades four main commodities:
- One megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity produced by a renewable energy source is certified as the bearer’s property by a renewable energy certificate (REC). Companies must comply with standards to demonstrate that they do not pollute and are following environmental regulations. A REC aids them in achieving this compliance, which may lead to government incentives, profits, or reduced taxes in the future.
- Energy Saving Certificates (ESCerts) – Similar to RECs, Energy Saving Certificates (ESCerts) only show the amount of energy saved from a project in megawatt-hours (MWh). Like regular certificates, these certificates can be purchased and sold.Companies can buy and sell EScerts and RECs on the exchange. This implies that a corporation receives a clean bill of health even if it may be polluting heavily but yet purchases enough of these certifications.
- the Day-Ahead-Market (DAM) It is a physical electricity trading market where electricity is distributed starting at midnight the following day and continuing for 24 hours. They trade in 15-minute increments of time. The auction bidding procedure was ended by the pricing and quantity of electricity.
- The Term-Ahead Market (TAM) offers a variety of products that enable users to buy or sell power on a term basis up to 11 days in advance.
Can I Trade on the IEX?
Retail traders are not permitted on IEX. Electricity is physically delivered as part of the exchanges. A person is allowed to trade on the exchange if they are the owner of a business that uses a lot of power. In addition, the person needs the required approval from the CERC in order to be able to trade on the platform. A member or client must have at least Rs. 150 Lakhs in capital, per the exchange’s rules, in order to transact on the platform.
Why Indian Energy Exchange shares fell 15% . Explained?
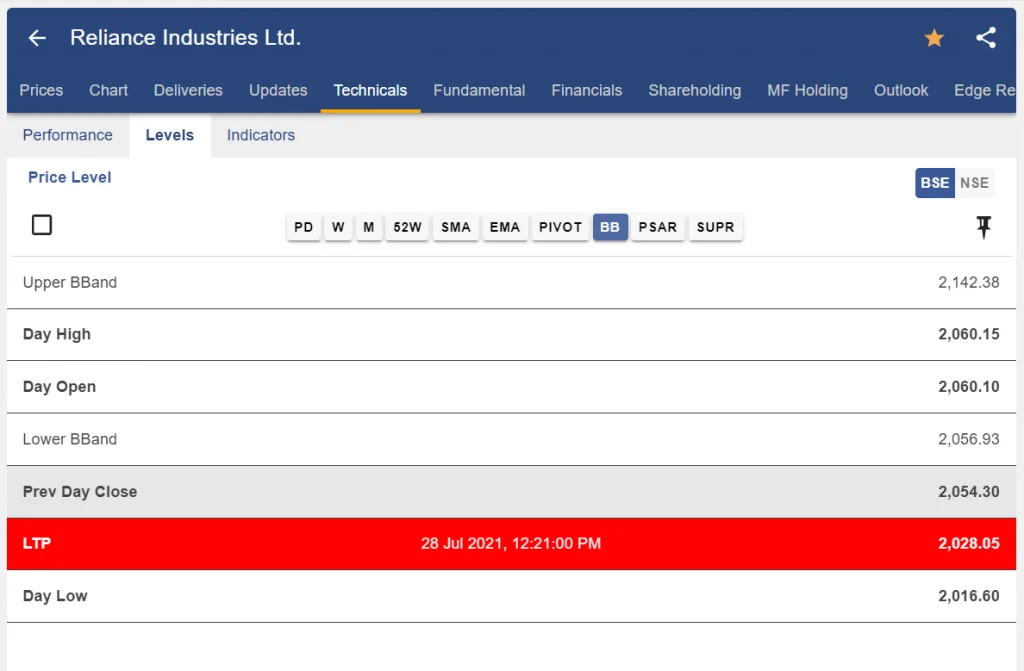
In Friday’s trading, Indian Energy Exchange (IEX) shares fell as much as 15% to hit a 52-week low of Rs 116 on the NSE as some analysts took notice of a June 2 circular that stated that the Power Ministry had instructed the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) to start the process of consultation and implement market coupling as soon as possible. The stock was down 9.93 percent at Rs 122.90 at 11:56 a.m.
IEX shares have dropped about 23 percent in two days after falling more than 8 percent in yesterday’s (June 8) final 30 minutes of trading. The IEX stock has lost 28 percent of its value over the past year, lagging the Nifty50 index, which has returned 13 percent over the same time frame.In the most recent development, price discovery would be handled by a super exchange, most likely a government organisation, leaving the power exchanges as nothing more than a platform for bid aggregation.
Market coupling will essentially kill innovation and competition in the sector, according to SN Goel, Chairman & MD of IEX. So, in my opinion, the interpretation of the market coupling that has been circulating for the past day is incorrect.
In any case, the ministry has asked CERC to check into this, according to Goel. “CERC will examine whether market coupling has a place in the current market design, which is a voluntary market, in this voluntary market design, whether we should pursue it or not, and what are the benefits,” he stated.
As of right now, IEX is India’s most reliable platform for determining power spot prices, which serves as a competitive advantage. The implementation of a full-fledged market coupler, however, entails that a neutral third party will compile all buy or sell bids and determine a standard market price for all exchanges.
This might make IEX’s “moat” ineffective because competing exchanges could eventually overtake it in terms of market share. The Day-Ahead Market (DAM) and Real-Time-Market (RTM) segments, which account for 75–80% of the exchange volumes, are almost entirely dominated by IEX.
What is market coupling?
PXIL explains market coupling as “the market coupler aggregates and matches all buy and sell orders from all the power exchanges to discover a uniform market clearing price, across all exchanges regardless of platform.”
The commercial moat of IEX is that it is now the most reputable platform in India for pricing determination. However, the MoP has instructed CERC to start the market coupling procedure.
For a relatively tiny fraction of the recently formed auxiliary market from April 23 to 29, NLDC served as the market coupler; yet, this marked the start of NLDC transitioning into a full-fledged market coupler function.
FOLLOW OUR WEBSITE: https://learningsharks.in/
FOLLOW OUR PAGE: https://www.instagram.com/learningsharks/