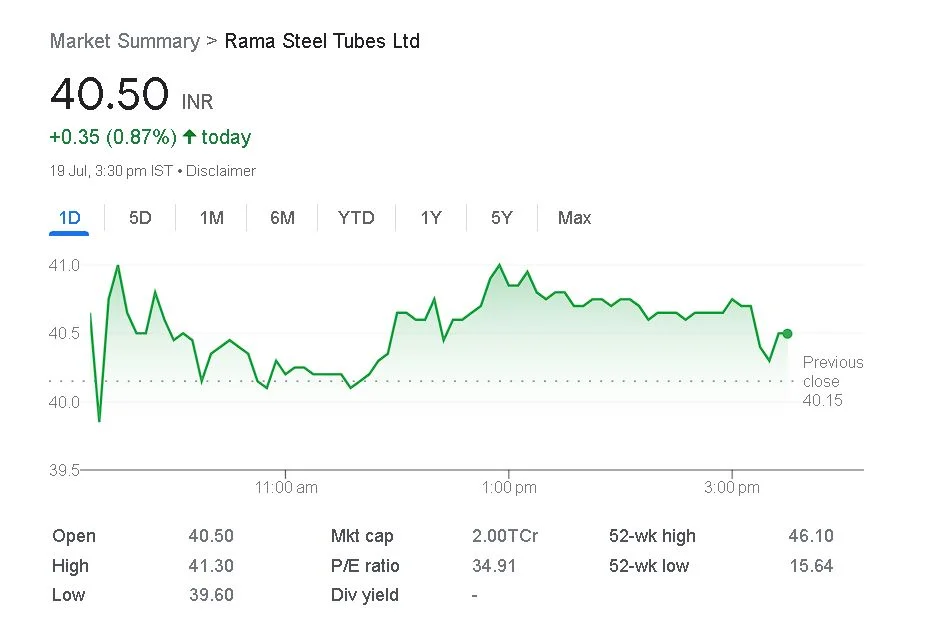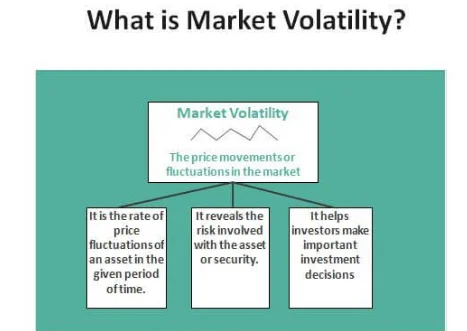
Market volatility is the degree of price variation or variability that a financial market or a particular securities experiences over a defined time period. It serves as a gauge for the rate and size of price changes. Prices can move quickly and significantly up or down when the market is extremely volatile. A number of variables, including economic statistics, geopolitical developments, investor sentiment, and company-specific news, can contribute to volatility. For investors, high volatility can bring both possibilities and threats. It increases the possibility of significant losses while also having the ability to yield bigger profits.
How does It Work In Stock Market?
Impact of Market Volatility on Investments
Investment value is directly impacted by market volatility. Prices can change significantly over brief periods of time when markets are extremely volatile. Investors may be able to profit from price changes by taking advantage of this volatility. However, it also raises the possibility of possible losses. The influence of market volatility on investments must be understood by investors.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Market Volatility
Advantages of Market Volatility:
- Profit Possibilities: Market turbulence can give investors the chance to earn big profits. Rapid price changes can result in quick profits if investors correctly forecast market moves and place trades at the right time.
- Market Liquidity Can Be Improved by larger Trading Volumes: Volatile markets frequently see larger trading volumes. Tighter bid-ask spreads and improved trade execution can both be a result of increased liquidity.
- Improved Portfolio Performance: Market volatility can give active traders and investors the chance to outperform benchmark indices. Price fluctuations offer opportunities for savvy market participants to profit and produce larger returns than times of minimal volatility.
- A better ability to make investment decisions Volatility may cause investors to review their investment plans and do extensive research. It promotes a deeper examination of businesses, industries, and market trends, resulting in more intelligent investment choices.
DisAdvantages of Market Volatility:
- Volatile markets come with increased levels of risk. Prices can move against investors swiftly and unpredictably, resulting in substantial losses. Unsophisticated portfolios are particularly vulnerable to sudden market declines.
- High market volatility can cause investors to make decisions out of fear, panic, and other emotions. Impulsive buying or selling might stem from emotional emotions, which could lead to bad investing decisions and possible losses.
- Increased Trading expenses: Volatility may be accompanied by greater trading expenses, such as wider bid-ask spreads or higher charges. During times of increased volatility, the cost of carrying out trades and putting risk management methods into action may increase.
- Uncertainty and Stress: Investors may experience uncertainty and stress due to volatile markets. Market gyrations and ongoing volatility can be mentally and emotionally taxing, which may impair an investor’s capacity for logical decision-making.
Conclusion
To sum up, market volatility is important stock market factors that have an impact on investors in many ways.
Market volatility has benefits, including the potential for profit, an increase in trading volume, the possibility of improved portfolio performance, and better investing decision-making. But it also has drawbacks, such as higher prices, more emotional decision-making, more risk, and stress and uncertainty.
FOR MORE INFO CLICK THIS SITE: https://learningsharks.in/
FOLLOW OUR PAGE: https://www.instagram.com/learningsharks/?hl=en